

In May, 1965 the Cony 360 Wide truck was introduced with a wheelbase of 168 cm, a rear rigid axle with leaf springs and an engine of 354 cc, placed underfloor in the center. A van was added by June, 1966. The styling was quite modern though uninspiring, and the vehicle remained available until the early seventies.

In April, 1964 came the Daihatsu Hi-Jet Cab with a wheelbase of 178 cm, a 356 cc engine under the front seat and available as a (low deck) pickup, accompanied by a truck in October, 1965 and a van in November, 1965. There was a rigid axle with leaf springs at the rear. In van form this vehicle looked rather dumb with its grille-less front with round headlamps and its high waist line. There was also the Daihatsu New-Line Cab as a pickup or truck with the wheelbase extended with 5 cm, and a length of 321.5 cm and a width of 134.5 cm; the engine was 797 cc.
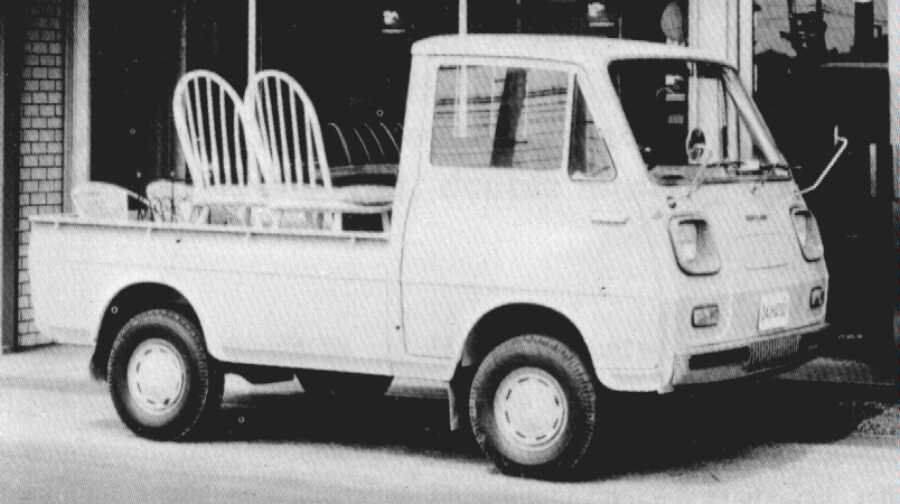

In May, 1968 arrived the second generation Daihatsu Hijet (without the Cab suffix, as the bonnet type Hi-Jet was succeeded by the Daihatsu Fellow in the meantime) with the wheelbase now only 168 cm, body styles were the same as before, with the addition of a pickup available with 2 seats on the deck and a hood with windows. There was also a pickup with a slightly higher even deck. Surprisingly, the van now had an independent rear suspension with coil springs, quite unique for this type of vehicle. The front of this generation looked rather noisy with its encadred oblong headlights and the van had an unsolid and quite depressing look with its heavy front and rear wheel overhang. The export models were called Daihatsu 360 Cab.


By September, 1971 already came the third generation Daihatsu Hijet pick-up and truck with the same dimensions as before. The van was added by February, 1972 and now had sliding side rear doors, a first in the Kei industry; the rigid axle with leaf springs returned. The vehicles looked much brighter than before with rounded lines, also round headlamps again. In April, 1976 a 547 cc engine became available and the length of these vehicles was 304/309 cm. In the export the models were called Daihatsu 360 Cab and Daihatsu 550 Cab, with a panel van and a minibus available.

In April, 1977 arrived the 4th generation, called Daihatsu Hijet 55 Wide with enlarged dimensions (length 319.5 cm, width 139.5 cm, wheelbase 178 cm, engine 547 cc), the pickup (integral body styling) was deleted. The body looked more solid now. In the export the vehicle was called Daihatsu 55 Wide Cab. The previous generation models remained available.


April 1981 saw the introduction of the 5th generation Daihatsu Hijet which finally received a matured appearance. The wheelbase was now 182 cm, the body styles initially the same as before with a high-roof van version (also available as panel van) added, and by 1983 an interesting extended (30 cm) cab (high-roof) truck, called Jumbo, the first and only in the Kei vehicle industry; this vehicle looked very balanced with a 164 cm deck (roughly half of the length of the vehicle). By 1982 arrived a four-wheel-drive version (wheelbase 181.5 cm), the high-profile tire versions were called Climber (such versions with 2WD and a non-slip diff adapted this name later). In September 1981 arrived the Daihatsu Hijet Atrai van, later in 1983 simply called Daihatsu Atrai, destined for the buyers who wanted a passenger vehicle, rather than a commercial vehicle; a turbo engine became also available for this vehicle. In the export (now also available in Europe) the vehicles were called Daihatsu 55 Wide Cab and Daihatsu 850 Cab (3-cylinder 843 cc engine); by 1984 arrived the Daihatsu 1000 Cab with a 3-cylinder 993 cc engine, which, rather uniquely, was also available as a diesel; panel van and minibus available as usual. In China, this vehicle is built as Huali (843 cc) with various designations and body styles, among which the interesting Huali TJ6350, an extended (extra length and narrow window between the front and the rear side doors) 8-seat high-roof minibus with a 30 cm longer wheelbase, and the body widened to 156.5 cm, and a length of 354.5 cm; there is also a truck with these dimensions, called Huali TJ1013F. There was also a non-widened high-roof minibus on this wheelbase, as well as a double-cab 4-door pickup, called Huali TJ1010SL, and an extended-cab called Huali TJ1014FQ. Early 1998 there was a new front end on the Huali TJ6330 minibus and Huali TJ1010C minivan. Originally, these vehicles were known as Tianjin TJ 110.


In May 1986 came the 6th generation Daihatsu Hijet and Atrai with the 3rd side window extended downwards. The wheelbase was now 181 cm. Engines and body styles remained the same with a supercharger available in the truck, and the edition of a 4-door (sliding door) double cab (high-roof) pickup, called Deck Van (deck 89 cm long, 127 cm wide); this vehicle was also available as Atrai Deck. The Jumbo cab was now extended with 28 cm, resulting in a deck length of 166 cm, grown to 170 cm by 1990 with the implementation of the new Kei vehicle regulations. At this time the engine became 659 cc and the length 329.5 cm. In the export, the vehicles were now called Hijet as well (993 cc). From 1992 the vehicle was also built in Italy (also with a 1.2 diesel engine), as well as Innocenti Porter, and Piaggio Porter with a 1269 cc 4-valve engine and a 1371 cc diesel engine. By 1992 arrived in Korea the Asia Towner (van, truck and minibus, 659 cc), later called Kia Towner.

By January, 1994 arrived the 7th generation Daihatsu Hijet with a wheelbase of 190 cm. The deck of the Deck Van was 92.5 cm long and 128.5 cm wide. The Daihatsu Atrai, now accompanied by the Atrai Legrand received a live rear axle with coil springs. In October 1997 arrived the Atrai Classic with a retro front. At the same time came a sporty looking (integral) pickup with a high-roof, called Hijet is. There was also a high-roof single cab truck available. In Europe, this generation was not sold. The Jumbo cab is extended 28.5 cm and the deck length is 199 cm, which is 5 cm longer than for the regular cab truck, as the cab extension is mounted after the cab back having been removed, while the deck is extended forward well into the cab underneath. Due to the fact that both front and rear cab extensions are attached rather than integral, the balanced looks of the previous generation Jumbo couldnot be maintained though cab and truck part lengths are almost equal.


By 1999, in Japan the cab of the truck was widened to 147.5 cm with a new door panel crease and given a small front extension (new safety regulations), total length now 339.5 cm.


In January, 1999 came the 8th generation Daihatsu Hijet Cargo and Daihatsu Atrai and Atrai Custom, with an arguable exterior though designed by Giorgetto Giugiaro, vans only, high-roof available. The design is now semi-front due to the new safety regulations, the wheelbase is a long 242 cm, the length 339.5 cm. Engine still under the front seat. Rigid rear axle with leaf springs for the Hijet Cargo, live rear axle with coil springs for the Atrai. By June, 1999 arrived a so-called wagon version of the Atrai, regarded as a passenger car rather than a commercial vehicle. Also in June, 1999 came the 3rd generation 4-door double cab Deck Van (deck now only 67 cm long, 129.5 cm wide). In May, 2000 arrived the 7-passenger Daihatsu Atrai 7 (high-roof van only) with the wheelbase extended to 243 cm, the length to 376.5 cm (mainly by a longer rear end), and the width to 151.5 cm (extended wheel arches), the engine is a 4-cylinder 1297 cc DOHC 4-valve; this vehicle became also available as Toyota Sparky in September, 2000.


Note: In 1995 in Indonesia came the larger Daihatsu Zebra Espass minibus with a wheelbase of 208 cm, a length of 387.5 cm and a width of 156 cm. Engines: 1295 cc and 1589 cc. In Malaysia this vehicle is built since March 1996 as Perodua Rusa, also as a panel van. In China there is the Wuling LZW 6370A.

In about 1961 arrived the drolly looking Gasuden Minivan M36 with a wheelbase of 188 cm and a rigid rear axle with leaf springs. The underfloor engine was 356 cc. It was not built for long.
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
The first Honda 4-wheel vehicle was introduced in August, 1963 as Honda T360, a semi-front truck or pickup with a wheelbase of 200 cm and a rear rigid axle with leaf springs. The underfloor engine was 354 cc. In September, 1964 the Honda T500 was added with a 531 cc engine and a length of 319 cm.

In October, 1967 came the cabover Honda TN360 with a wheelbase of 178 cm as a pickup or truck, the 354 cc engine was now placed further to the rear and a DeDion rear axle with leaf springs was adopted. This vehicle was renamed several times: Honda TNIII by January, 1970, Honda TN-V by August, 1973, adopting double vertical headlights, and Honda TN-7 by August, 1975. In the export the name remained Honda TN360.
In November, 1970 arrived the funny Honda Vamos open doorless cabover truck, with various seat and canvas top variations. It was based on the TN360 and 2,500 were built until 1973.
September, 1972 saw the introduction of the Honda Life Step Van, based on the Honda Life, a semi-front design with a rear rigid axle with leaf springs. A Honda Life Pickup was added in August, 1973. This is the only front-wheel-drive Kei class minivan/pickup ever made in Japan! The van remained available through 1975, the pickup was already deleted in October, 1974 with less than 1,500 made.

So came in September, 1977 the 3rd generation minitruck, now called Honda TN Acty, with a wheelbase of 185 cm, length 319.5 cm, width 139.5 cm, engine 545 cc, same technical layout and bodies as before. In June, 1980 the first Honda full-front minivan was added with a rather angular styling. A high-roof version was added in February, 1981, as well as a less commercial version, the Acty Street. Later models were also known as Honda Acty. By March, 1983 four-wheel-drive became available.


By May, 1988 arrived the 4th generation Honda Acty and Honda Street, now with a wheelbase of 190 cm, truck and high-roof van only, a panel van was available, mediocre albeit neat styling. By 1990 (new regulations) the length became 325.5 cm for the truck and 329.5 cm for the van and the engine, still placed before the rear axle, grew to 656 cc. There was also an extra high-roof van with side windows in the roof and suited for carrying a disabled person in a wheelchair, called Honda Acty Almas and Honda Street Almas.

.gif)




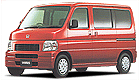

Then, in June, 1999 arrived the 5th generation Honda Acty semi-front, wheelbase 242 cm, length 339.5 cm, width 147.5 cm, engine still 656 cc, styling quite neat, technical layout remained the same, high-roof van and truck, panel van available. A passenger car classified version (with normal roof) is also available, which adopted the old Honda Vamos name.

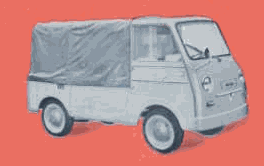
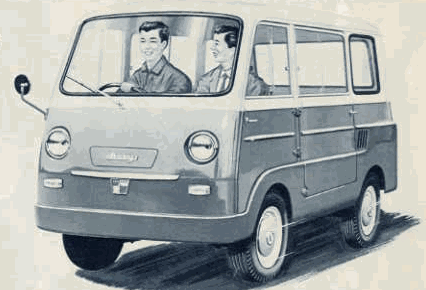
In about 1959 arrived the Kurogane KB-360 pickup (hooded version with 2 seats on the deck available) and van with a wheelbase of 175 cm, a length of 299 cm and a width of 127.8 cm. The rather highly built engine was placed at the rear (coil springs) and had 356 cc.
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
In April, 1969 Toyo Kogyo introduced the Mazda Porter Cab with a wheelbase of 183.5 cm as a pickup or truck only, a rigid rear axle with leaf springs and a 359 cc engine, placed under the front seats. It featured a quite funny styling with round headlamps with round cadres, giving kind of a spectacles look. By March, 1977 the vehicle was widened to 139.5 cm, and the length grew with 20 cm (to 319.5 cm), nearly all of which benefited to the deck length, as the wheelbase, quite unusual, was not changed. The engine grew to 546 cc, the (integral) pickup was deleted and the 'spectacles' were more rectangular now. The vehicle remained available until the late eighties. In the export it was known as Mazda E360.

Then, in June, 1989 arrived the Autozam Scrum, a clone of the Suzuki Carry/Every as a truck and a van, the 543 cc engine became a 657 cc in March 1990.

The second generation Autozam Scrum became available in October 1991, again a Carry/Every clone. A less commercial version was called Scrum Stand Off. The vehicle was renamed Mazda Scrum in the autumn of 1997.


By January 1999 arrived the 3rd generation Mazda Scrum, again as a truck and a van, joined in December, 1999 by a so-called wagon version. For details, see Suzuki.
.jpeg)
.jpeg)
In August, 1966 Mitsubishi joined the Kei class minivan/truck market by introducing the Mitsubishi Minicab with a wheelbase of 179 cm as a pickup (by December, 1967 also available with 2 seats on the deck and a hood with windows), truck (December, 1966), and, by February, 1968 a van. The engine, placed under the front seats was 359 cc and the rear axle rigid with leaf springs. The styling was immature as usual in those days. By May, 1971 the van was renamed Mitsubishi Minicab EL.

Then, in June, 1971 the second generation arrived as a truck only, initially called Mitsubishi Minicab EL, the following year it was renamed Mitsubishi Minicab W. The wheelbase was now 174 cm and the boxy cab looked rather neat.

By April, 1976 arrived the third generation, now called Mitsubishi Minicab 5 (471 cc) with a wheelbase of 170 cm; the length was 305 cm for the truck and 306 cm for the van (this second van looked rather busy, it now had sliding side doors), the width remained 129.5 cm, rather strange so shortly before the new standards to come. So, in March, 1977 the vehicle, now called Mitsubishi Minicab Wide 55 (546 cc) was widened to 139.5 cm, the wheelbase extended to 176 cm and the length for the truck became 319.5 cm, for the van 315.5 cm, extra 6 cm length after the front doors, a high-roof van became available in 1980, and four-wheel-drive in 1982. By 1981 the vehicle was renamed simply Mitsubishi Minicab again. In the export the vehicle was called Mitsubishi L100, the engine grew from 546 cc to 644 cc in 1981 and 783 cc in 1984. In China the vehicle is built as Shenwei SYW 1010(X) and Wuling LZ 110, later called Wuling LZW 1010, which was also built as a minibus and a 4-door double cab pickup (Wuling LZW 1010 SD); engines 644 cc or 797 cc. There has also been a 546 cc minibus (also high-roof), called Liuzhou LZ 110.


The 4th generation Mitsubishi Minicab came in June 1984 with a wheelbase of 178 cm, a high-roof cab truck became additionally available. The vehicle looked rather neat though the front wheelarch cutting was irregularly shaped. By 1990 the length became 326.5 cm for the van and 322.5 cm for the truck and the engine grew to 657 cc. A less commercial Mitsubishi Minicab Bravo van was available. In the export the vehicle was again known as Mitsubishi L100 with 783 cc, a panel van was now available. In Indonesia in 1986 the body was widened to 147.5 cm, the wheelbase extended to 190 cm and the length to 345 cm (pick-up); the engine was 993 cc and it was known as Mitsubishi Jetstar (minibus and pick-up), to be replaced in 1991 by the Suzuki-based Colt T120 SS. In China the vehicle is built as Wuling LZW 6330/6430 (formerly called Wuling LZW 6320) minibus and Wuling LZW 1010 with various suffixes as a van, a truck and a 4-door double cab pickup, with the wheelbase extended to 201 cm and the length to 368 cm; a single cab truck with this wheelbase and a length of 350 cm is also available; engines 797 cc, 870 cc, 900 cc, 970 cc and 993 cc (843 cc and 1061 cc previously available). It is also built as Shenwei SYW 1010A truck. In Taiwan, the vehicle was available with a 3-cylinder 796 cc engine, and with a 1061 cc engine as Mitsubishi Varica minibus, van and truck with a wheelbase of 200 cm (extra length before the rear axle), length and width 370 cm and 147.5 cm respectively. By 2000, the engine became a 4-cylinder 1074 cc or 1198 cc, and the length varied from 385 to 396.5 cm. The earlier version was sold in China as Wuling LZW 6370.


In January, 1991 arrived the 5th generation Mitsubishi Minicab and Mitsubishi Bravo (now available with 657 cc turbo engine), with a wheelbase of 192 cm for the van and 183 cm for the truck, a length of 329.5 cm and a width of 139.5 cm. The high-roof cab truck was no longer available, a panel van was. The van looked quite strange with a roof sloping downward while the waistline was going upward. By 1994 the Bravo got a 4-cylinder 659 cc engine and a live axle with coil springs at the rear. In 1997 arrived a retro version, called Bravo Route 66.


In January, 1999 came the 6th generation Mitsubishi Minicab, now with a semi-front look as a van (low and high-roof; panel van available; wheelbase 239 cm, live rear axle with coil springs) and a truck (version with panels underneath available; wheelbase 220 cm, rigid rear axle with leaf springs), with acceptable looks. By April, 1999 arrived the Mitsubishi Town Box (also called T-Box), a so-called wagon version with the 657 cc or the 659 cc turbo engine, live rear axle with coil springs, high-roof (or sunroof) only. In June, 1999 the Mitsubishi Town Box Wide was added, which had a wider track and wheelarches only, length 360.5 cm, width 153.5 cm (compared to 339.5 cm and 139.5 cm respectively), 6 seats, normal roof, 1094 cc engine. Heavy bumpers and wheelarches make this vehicle look quite unattractive. In Malaysia this model is built as Proton Juara since July, 2001 (length 366 cm).
Note: For details of the Indonesian Mitsubishi Colt T 120, see Suzuki.
.jpeg)

In February, 1961 arrived the Subaru Sambar with a 356 cc rear engine, there was a swing axle with torsion bar springs at the rear, the wheelbase was 167 cm and a van was added in March, 1962. This was the first Kei class minivan among the main manufacturers, it had a rather dumb looking front end.

In January 1966 came the second generation Subaru Sambar, now with the wheelbase enlarged to 175 cm, a truck became available by March, 1967, and there was a panel van. Styling was typical for Kei minivans of those years. In about 1970 the rear swing axle was replaced by one with semi-trailing arms and torsion bar springs. In the export this vehicle was called later Subaru 360.

Then in February, 1973 arrived the third generation Subaru Sambar, now with a wheelbase of 173 cm, and side sliding doors, the styling was more mature, the pickup was deleted. In May, 1976 the engine grew to 490 cc and it was called Subaru Sambar 5, the vehicle was lengthened to 303.5 cm (truck also 310.5 cm) and the width became 134 cm (wider front bumper and truck deck). In the export it was still called Subaru 360, later Subaru 500.
This generation Subaru Sambar was widened to 139.5 cm by May, 1977; the wheelbase was now 182 cm (extra length behind the front door), the length 319.5 cm, the engine 544 cc. It was initially called Subaru Sambar 550. For the first time in the Kei industry a high-roof van was added in 1979. In 1980 came a 4-wheel-drive with a wheelbase of 180.5 cm. In the export the vehicle was known as Subaru 600.

In September 1982 came the 4th generation Subaru Sambar, still with rear engine, the wheelbase was now 180.5 cm for all models. The styling was neat, rather square as typical in this period. The pickup was no longer available, a high-roof truck was. In Japan the van was now called Subaru Sambar Try. A 544 cc supercharger engine became available later. A more passenger-car-like Subaru Domingo high-roof van with 997 cc, later 1189 cc engines and coil springs at the rear was added in October, 1983. It had a length of 341/342.5 cm and a width of 143 cm. This vehicle would stay available well after the release of the next generation Sambar. In the export the engine became a 665 cc and the vehicle was called Subaru 700 (length 322.5 cm). The larger versions were called Subaru E10 and Subaru E12 respectively.


March, 1990 saw the introduction of the 5th generation Subaru Sambar/Sambar Try, in time for the new regulations. So the length grew to 329.5 cm, the wheelbase to 188.5 cm while the engine became 658 cc; all models had now coil springs at the rear. The irregular window belt line made the vehicle look a bit complicated. By 1991, a less commercial van version arrived, called Subaru Sambar Try Dias. By 1992 the 'Try' suffix was deleted. In 1994 arrived a retro version, called Subaru Sambar (Dias) Classic (Dias with a blinded rear side window), in 1997 also as a truck. Only in June, 1994 arrived the Domingo based on this generation with a length of 352.5 cm and a width of 141.5 cm, 1189 cc. This vehicle was called Subaru Libero in the export, Subaru Estratto in Taiwan.


In February, 1999 in time with the new regulations a semi-front end was added for safety reasons resulting in a length of 339.5 cm, while the body was widened to 147.5 cm with a minor change in the panelling; the busy belt line was put straight. The Sambar Dias has its own front end as has the Sambar Dias Wagon Classic. The Domingo is no longer available.

In October, 1961 arrived the Suzulight Carry semi-front pickup with a wheelbase of 185 cm and a 359 cc engine, placed under the front seat. It had rigid axles with leaf springs both front and rear. By July, 1962 arrived a van and in November, 1964 a truck. In the export it was also known as Suzulight (360) FB.

In June, 1965 came the second generation Suzulight Carry pickup and truck, again a semi-front design, now with a wheelbase of 187 cm and independent front suspension. In January, 1966 became a van available, as well as a 4-seat pickup with an extra seat in the rear deck. This vehicle would remain available through 1970. In the export the vehicle was known as Suzuki 360 (L20).

Then came in March, 1966 the first full-cab Suzuki Carry pickup with a wheelbase of 174.5 cm, next to the Suzulight Carry. By July, 1966 came a hooded pickup with a seat in the rear deck. In January, 1967 arrived a truck, and in March, 1968 a van. The 359 cc engine was placed underfloor and the rear axle was rigid with leaf springs. The styling was rather appealing though immature. In the export the vehicle was known as Suzuki 360 (L30/L31).


In July, 1969 arrived the Giugiaro-designed second generation Suzuki Carry as a pickup and truck, with the van following in November, 1969. Dimensions and layout remained the same as before, the styling was more modern, with a questionable cut-off roof back end for the van.

So, the third generation Suzuki Carry was released in December 1972, body styles and layout remained the same, the much more appealing van now had sliding doors. In the export the vehicle was known as Suzuki L50 or Suzuki L51 (truck); by 1975 as Suzuki L60 or Suzuki L61 with a 446 cc engine. In May, 1976 the engine became a 539 cc, the name Suzuki Carry 55, this vehicle was called Suzuki ST10 in the export. By September, 1976 (Van: November, 1976) the vehicle was widened to 139.5 cm and the wheelbase lengthened to 184 cm (extra length behind the front door); the length of the vehicle became 315.5 cm for the van and 319.5 cm for the truck and pickup. The vehicle was now called Suzuki Carry Wide 550. In the export this vehicle was known as Suzuki ST20; by 1977 came the Suzuki ST80 with a 797 cc 4-cylinder OHC engine. In China, the vehicle was built as Jilin JL 1010 pickup and 4-door double cab pickup, as well as Jilin JL 6320/6330/6360 minibus (formerly known as Jilin JL 110) and van, both also available with high-roof. An interesting model was the 8-passenger high-roof minibus with the wheelbase stretched to 214.5 cm (extra length and narrow window behind the front door), a length of 345.3 cm, and widened to 154.5 cm. The engines were 796 cc 3-cylinder, 797 cc and 970 cc. Anhui Huaihai built the Feihu HH110 and Feihu HH111, also as a 4-door double cab.







In Indonesia the Suzuki Carry as a minibus and truck was redesigned and enlarged by 1991; the length is 370 cm and the width 149.5 cm, the engine 970 cc. In the same style, both minibus and truck are built as Suzuki Carry Futura, later called Suzuki Futura with the wheelbase extended to 197 cm, length 387.5 cm, width 157 cm and an engine of 1590 cc (initially 1360 cc), also as Mitsubishi Colt T 120 SS with a 1343 cc engine (length 372 cm).


In Japan, in September, 1991 arrived the interesting 6th generation Suzuki Carry and Every. The wheelbase of the truck was now 185.5 cm, the length of course 329.5 cm; the technical layout for the truck remained the same as before, though the engine was moved mid-ship. The van (Every and Carry) saw the engine moved backward just in front of the rear axle which was now a coil-sprung De Dion (rigid with 4 axle joints); the wheelbase was 200 cm and the styling was very attractive overall. In late 1997 a retro front version arrived, known as Suzuki Every C.



Details of Toyota Sparky to be found at Daihatsu.
Please have your comments.
Homepage
Note: Length/Width/Displacement originally 300 cm/130 cm/360 cc . . . by 1976: 320 cm/140 cm/550 cc . . . by 1990: 330 cm/140 cm/660 cc . . . by 1999: 340 cm/148 cm/660 cc
Note: Honda T360, 1st Minicab, Sambar, 1st Suzuki Carry and Porter pictures kindly borrowed from Mr. Someya's Web Page with permission.
Far East Auto Literature, 2000